"The hospital’s medical environment has been greatly improved, and doctors are still really busy, but doctors and patients seem to be a little wary of each other. The most troublesome thing is that no one wants to do emergency treatment now. "
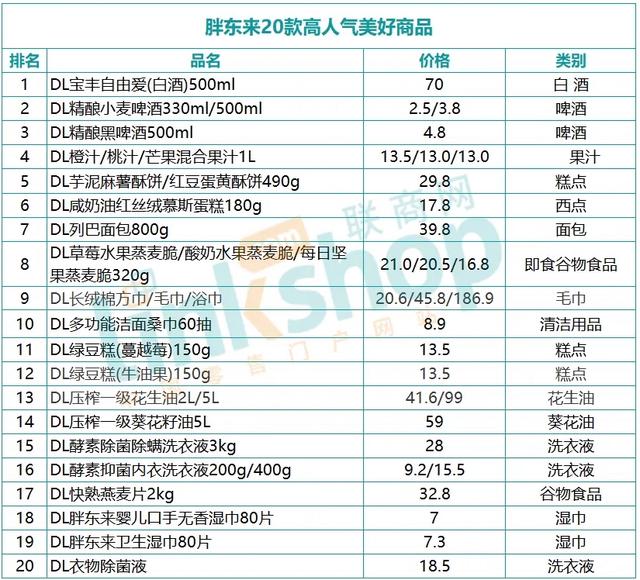
April 22nd is the 60th birthday of Sun Changyi, director of the emergency department of xuanwu hospital (hereinafter referred to as xuanwu hospital), and it is also the day for him to bid farewell to the emergency department and retire gloriously.
Looking back on his 33-year emergency care career, Sun Changyi felt a lot: "When I first went to work, not to mention being an old doctor, even our newly graduated students had a full sense of mission. Everyone really did it. I remember that in summer, in order to care for critically ill patients in ICU wards, we all spread a mat on the floor next to the hospital bed to sleep, and the nurses came to deal with the patients on call at midnight. "
Today’s emergency department is another look that Sun Changyi is familiar with: "The hospital’s medical environment has been greatly improved, and doctors are still really busy, but doctors and patients seem to be a little wary of each other. The most troublesome thing is that no one wants to do emergency treatment now. Our hospital is a top three hospital, and it is hard to recruit people in the emergency department, let alone primary hospitals. "
At the same time that the emergency department is "cold", the public’s demand for emergency medical resources is growing day by day, and the number of patients in the emergency department is growing rapidly. According to the public data of the Statistical Information Center of the National Health and Family Planning Commission, in 2007, there were 51.879 million emergency department visits, and in 2012, this number doubled to 107.805 million visits.
Yu Xuezhong, chairman of the Emergency Medicine Branch of the Chinese Medical Association and director of the emergency department of Peking Union Medical College Hospital (hereinafter referred to as Union Medical College Hospital), commented to Outlook News Weekly that the emergency department was "hot outside and cold inside", indicating that "the emergency system is overloaded and worried about functional failure".
Yu Xuezhong, for example, said that more than a decade ago, doctors in the emergency department simply dared not imagine that ambulances carrying seriously ill patients would be transferred to other medical institutions. Now, due to the frequent "no beds" in emergency departments of large hospitals, it is common for ambulances to be transferred to other medical institutions. "If we turn a blind eye to this kind of danger of’ boiling frogs in warm water’, there may be a risk that the emergency system will collapse in the future."
Why is the emergency department "seriously ill"? What kind of "treatment" is needed for the diseases in the emergency department? Many problems are unavoidable.
"Overloaded" Emergency Department
The "overload" of the emergency department is becoming more and more shocking.
At 9 o’clock in the morning, the narrow corridor of the emergency department in xuanwu hospital was crowded with people. However, in Sun Changyi’s view, this situation is "not bad. If it is six or seven o’clock in the evening, it will probably be too crowded to walk."
According to Sun Changyi, there are currently 40 doctors, 120 nurses and more than 80 beds in the emergency department of xuanwu hospital, with an average of 450 patients a day. "Among more than 70 top-three hospitals in Beijing, the emergency department of our hospital has the smallest area, but the number of emergency patients is quite large, basically ranking 5 ~ 7. In 2015, among the hospitals managed by Beijing Hospital Authority, our disease difficulty coefficient ranked first, which means that the emergency patients we treated were very serious. " Sun Changyi said.
Under the crowded situation of emergency department and the increasing pressure of emergency patients, the area of emergency department is expected to expand in the expansion plan to be completed in xuanwu hospital, and the number of emergency beds will increase accordingly.
Yu Xuezhong has experienced many "expansions" in the emergency department of Union Medical College Hospital. His feeling is: "The emergency department seems to always lack a bed."
Yu Xuezhong said that the emergency department of Union Medical College Hospital was established in 1983. At the beginning of its establishment, the average daily emergency volume was about 30-40 person-times, reaching more than 100 person-times in 1996 and rising to 500-600 person-times in 2012. In order to adapt to the increase in the number of emergency patients, the number of emergency beds has increased from 21 to more than 100. "However, the growth rate of beds seems to never keep up with the growth rate of patients. The newly added beds are always filled up quickly, and the emergency department is always overcrowded."
A survey of emergency resources led by Union Medical College Hospital and covering 33 tertiary hospitals in 31 provinces (autonomous regions and municipalities) shows that most emergency departments were established in the 1980s, when the department area was 500 to 600 square meters. Although the scale of emergency department will be expanded once every five to ten years, and the existing area mostly reaches 5,000-8,000 square meters, the annual emergency department is 5-15 times higher than that at the beginning of the establishment of the department, and the emergency departments in most hospitals are still very crowded, with aisles and corridors full of "extra beds".
Yu Xuezhong said that "Big Mac" emergency departments with a building area of over 10,000, employees of over 100 and annual emergency volume of over 100,000 are common in China, but no matter how the emergency departments are enlarged and expanded, chaos and crowding are almost inseparable.
The "chaos" and "crowding" in the emergency department are closely related to the "hidden rules" of emergency department.
According to Yu Xuezhong, the outpatient resources in large hospitals are limited, and patients are often hard to find the first number, but the emergency number is not limited in principle, so some patients who "have no access to the number" turn to the emergency department to see a doctor. As a result, some problems that should have been solved in the specialist clinic were pushed to the emergency department, which objectively led to the crowded emergency department. "Although there is no document stipulating that emergency treatment must be’ come to the net’, it is actually carried out in this way. Emergency treatment can never say’ no’ to patients, otherwise it will face moral condemnation from from ruin, and the snowball will naturally get bigger and bigger. This situation is more prominent in the famous big hospitals. " Yu Xuezhong said.
From the perspective of future medical reform, the situation of "chaos" and "crowding" in the emergency department is likely to intensify.
Yu Xuezhong explained that at present, the medical reform is pushing for a graded diagnosis and treatment system. According to the relevant system design, a large number of patients need to make the first outpatient consultation in primary hospitals, and the outpatient service in large hospitals can only be obtained through referral from primary hospitals. However, emergency treatment can still go directly to large hospitals, which obviously leads to a decline in the number of outpatients in 3A hospitals and an increase in the number of emergency treatments, which puts pressure on the emergency department from the policy and may make the emergency department more crowded in the future. "
"Not in a hurry" emergency patients
However, most of the "overloaded" emergency departments are "not in a hurry" emergency patients.
In Sun Changyi’s impression, among the daily average of 450 emergency patients in xuanwu hospital, non-emergency patients account for at least 1/3, and those who need immediate rescue only account for about 5%~10% of the total emergency patients.
Union Medical College Hospital once broke the news that the patient lived in the emergency ward for 7 years, and the patient was "discharged" from the emergency department until he filed a lawsuit with the court.
According to Yu Xuezhong’s estimation, generally speaking, less than 50% of the patients really need to see the emergency department. "The emergency department is full of non-emergency patients, which means that limited emergency resources are being abused."
"Emergency is not urgent" first stems from the public’s misunderstanding of emergency.
Emergency, that is, emergency treatment. In Yu Xuezhong’s view, there are three main original intentions for hospitals to set up emergency departments: one is to save lives; The second is to stabilize the patient’s pulse, blood pressure, heart rate, blood oxygen and other vital signs, and relieve his potential life danger; The third is to relieve patients’ acute pain, such as rash and fishbone sticking. "In short, the existence of emergency is to ensure that the public can get professional and scientific treatment in the shortest time in the emergency of sudden illness and accidental injury. However, the public’s understanding of emergency may be the aggravation of chronic diseases, and it may be that there was no disease in the past but now there are symptoms. These are usually not emergency areas in the strict sense. "
For example, Yu Xuezhong said that an emergency is not necessarily a serious illness. For example, a patient with a fishbone must be very urgent, but this emergency is usually not a serious illness; Severe illness is not necessarily an emergency. For example, chronic respiratory diseases that the elderly are prone to often belong to severe illness, but this kind of serious illness does not necessarily need immediate treatment. "Patients who are both acute and severe are the real emergency patients, but this proportion is not high in the emergency department."
In this regard, the emergency department has no good strategy. The only thing it can do is to comprehensively analyze, eliminate the false and retain the true through the triage desk, reconnaissance and determine the patient’s condition, and classify the patients according to this, and deal with the patients according to their priorities.
It is difficult to distinguish between emergency and non-emergency, which also objectively aggravates the "emergency is not urgent" Yu Xuezhong said, generally speaking, you don’t need to see an emergency department for a common cold, but if the patient happens to have myocarditis, he may die if he doesn’t go to the emergency department immediately. For another example, the elderly occasionally feel chest tightness, but this may be a potential myocardial infarction. If the patient is careless and delays the treatment of myocardial infarction, it may have serious consequences. "Because some diseases are not well differentiated in symptoms, patients and their families simply go to the big hospital to see the emergency department without distinction. Although it has been repeatedly proved that it is just’ wolf coming’, this behavior is understandable."
Emergency detention is also an important factor of "emergency is not urgent".
According to Yu Xuezhong, European and American countries usually stipulate that the emergency department is an emergency medical place, and it will be transferred to a specialized ward after 24 hours. However, in China, even if the country relaxes the time for emergency patients to stay under observation to 72 hours, the phenomenon of "overtime" still exists everywhere, and the problem of emergency detention is very prominent. "This is not that the emergency department’ intercepts’ patients, but that the specialist wards of the top three hospitals often have no beds. If specialists don’t take patients away, they can only keep patients in the emergency ward."
Yu Xuezhong explained that the Union Medical College Hospital clearly stipulates that after each specialty is handed over in the morning, there will be the chief doctor on duty in the department to check the patient list and diagnosis results in the emergency department, and the appropriate patients will be received in the specialized ward for treatment. "That is to say, our emergency doctors have no power to forcibly transfer patients to specialist wards, and they can only recommend them to specialists, and the leading power is in the hands of specialists."
Sun Changyi’s statement is more straightforward: "When specialists come to the emergency department to accept patients, they obviously prefer those patients with high gold content and high quality, that is, patients with no complications, and some elderly patients with many complications and poor payment ability are often left behind in the emergency department. According to our statistics, among the patients admitted by our department, 66% are over 80 years old, and 1/3 are with more than three organ failures. For patients with three organ failures, the mortality rate is usually as high as 85%. "
Zhu Huadong, deputy director of the emergency department of Union Medical College Hospital, told this reporter that specialists have their difficulties in "picking" emergency patients. "At present, the medical and health management and medical insurance departments are conducting strict assessments on hospitals and professional departments, and have more detailed indicators on ward utilization rate, bed turnover rate, average hospitalization expenses and hospitalization time. Hospitalization of patients with severe chronic diseases and complications means that the assessment results will be’ delayed’. Under the pressure of assessment, specialists naturally tend to provide limited beds to patients who are beneficial to the assessment results. "
For example, because Beijing stipulates that patients can’t stay in hospital for more than 11 days, patients who are not expected to leave the hospital for 11 days are unwilling to accept them in specialized wards. "So we sometimes joke that if you are going to get sick, if your illness happens to catch up with the research project in the hospital, then you can live in the hospital that is difficult to live in. Although this is absurd, it really happened. " A doctor who asked not to be named told this reporter.
The lost emergency doctor
Behind the "emergency is not urgent" is the unspeakable bitterness and embarrassment of emergency doctors.
In Sun Changyi’s view, the labor intensity of no department in the hospital can be compared with that of emergency department. "It’s normal for doctors and nurses in emergency departments to rest in the white night (one day’s white shift, one day’s night shift, one day’s night shift and one day’s rest day), and staying up late is more common. Even on holidays, other departments are on holiday and the clinic is closed, but the door of the emergency room is always open. "
The work pressure of emergency doctors is also reflected in the wide spectrum of diseases of patients, the unpredictable types and quantity of patients, and various uncontrollable factors. "The number of patients treated by specialists in outpatient clinics is relatively fixed every day, and the types of diseases of patients are relatively fixed. The situation is obviously relatively easy to control." Zhu Huadong said.
At the same time, the income and treatment of emergency doctors are often "not available".
According to Yu Xuezhong, the emergency department of Union Medical College Hospital has always been the registration fee of 1 yuan and the treatment fee of 4 yuan, compared with the specialist special number of 300-500 yuan and the specialist expert number of 14 yuan, even though the doctors who accept patients already have senior titles. "As far as Beijing is concerned, other hospitals are implementing this charging standard except five pilot hospitals that have cancelled drug addition."
In addition, because the "three noes" patients (no identity, no family members, no money) and drug addicts often "visit" the emergency department, the probability of emergency doctors suffering economic losses due to patients’ arrears is correspondingly increased.
Sun Changyi said that emergency doctors usually hesitate when they hear that the patients with "three noes" are sent by 110, because the medical expenses incurred by the patients with "three noes" are often not "paid". "Take our hospital as an example. Although the Civil Affairs Bureau has certain subsidies, the emergency department has hundreds of thousands of unrecoverable money every year. xuanwu hospital’s policy in this regard is really good. The hospital bears these bad debts, which has not deducted the performance of the emergency department and has not affected the income of emergency doctors. However, as far as I know, emergency departments in many places are not so lucky. Some doctors will be deducted from their wages and bonuses because they don’t get their money back. "
According to the analysis of the industry, when entering the profession for the first time, the advantage of emergency doctors is that they can meet all kinds of patients and diseases in a short time, and their horizons are broader, and there are many opportunities to start work. However, because of their fine disciplines and many experts, many diseases can’t be encountered for a lifetime, and there are few opportunities for actual combat. Therefore, when the specialists with the same qualifications are still working hard in the ward to write medical records, emergency doctors may have been on duty with their own teams. However, if we look at it from the time dimension of 10 years, most of the specialists at this time have begun to appreciate the beauty and profundity of the vast world in this field, but the emergency doctors with the same experience are often repeating the business that they used to be familiar with, and it is inevitable that they will be tired and feel bleak in the future.
Under various factors, it is very common that emergency departments can’t recruit people and can’t keep people.
Sun Changyi said that xuanwu hospital’s emergency departments have had difficulties in recruiting for several years in a row. "The funniest thing is that only one doctor in our department has resigned so far this year, which has surprised many colleagues, because everyone knows that the emergency department is a’ big family’ for doctors to’ run away’."
Yu Xuezhong’s embarrassment is: "With the golden signboard of Union Medical College Hospital, although the emergency department is not dissatisfied, medical students often have no choice but to choose our department."
The famous Union Medical College Hospital is still facing such a dilemma, and the rumor that medical students are "holding their noses and doing emergency work" seems to be true.
The "aisle" theory of emergency medicine
In fact, not only some doctors "dislike" the emergency department, but even within the medical discipline, emergency medicine is often a forgotten corner, and all kinds of misunderstandings, misunderstandings and misunderstandings emerge one after another.
In November 2015, the "2014 China Hospital Rankings" led by the Hospital Management Institute of Fudan University was released. In this ranking, which has been published for six years in a row, the number of medical specialties participating in the evaluation has reached 34, but there is no figure of emergency medicine.
In many people’s minds, the emergency department is just an "aisle" and an advanced "triage desk" for patients to enter specialized wards. It only deals with mild patients such as colds and diarrhea. When they encounter heart failure, myocardial infarction, or severe trauma, they are immediately helpless. At this time, emergency doctors often spread their hands and quickly let nurses divert patients to relevant specialized wards.
Guo Shubin, director of the emergency department of Beijing Chaoyang Hospital (hereinafter referred to as Chaoyang Hospital), finds it difficult to agree with this concept. In his view, with the continuous progress and development of medical specialty technology, the achievements of specialty are gradually recognized and familiar by the society, but the bottleneck brought by "specialization" is becoming increasingly prominent. In recent years, the pace of developing general practice has been accelerated, which provides an opportunity for the development of emergency medicine.
For example, Guo Shubin said that at present, the research progress and diagnosis and treatment level of diseases in various specialist systems in China have reached a certain level, such as interventional therapy in cardiology department, examination and treatment under digestive gastroscope, etc., but for a patient with acute upper gastrointestinal bleeding complicated with acute myocardial infarction, the specialist’s "high-level" diagnosis and treatment means will be stretched, because specialists are likely to only look at the diseases in their own specialty. "More and more people have noticed that the division of medical specialties is too fine, which is not suitable for patients, because patients are often not a single disease, especially for elderly patients with multiple organs and systems. If the hospital sets up a comprehensive ward under the emergency department, it will solve the medical needs of these patients. "
In this sense, Guo Shubin believes that the so-called long-term integration and long-term integration must be separated. Since the development of medicine, the concept of holistic medicine has been paid attention to again, and within the medical discipline, emergency medicine has always been adhering to the concept of holistic medicine. "Therefore, the’ aisle’ theory and the’ triage desk’ theory of the emergency department have long been outdated and are not worth refuting."
Yu Xuezhong said that at present, emergency medicine is a second-class discipline on the same level as internal medicine, surgery, gynecology and pediatrics. "This is the country’s recognition of emergency medicine from the management. In particular, the professional content of emergency medicine has been added to the current senior title promotion examination, which has solved the problem of senior title promotion for emergency doctors. Under this circumstance, the future emergency medicine is obviously a sunrise discipline, and emergency doctors will be very attractive jobs. "
Future emergency
In addition to building a comprehensive ward to treat patients with multiple diseases, Chaoyang Hospital is also exploring the emergency mode linked with primary hospitals in order to change the crowded situation of emergency departments.
Guo Shubin believes that the top three hospitals and primary hospitals can have a division of labor after the establishment of the medical association. The emergency department of the top three hospitals is mainly responsible for treating critical and serious diseases. Emergency doctors need to quickly receive consultations and make judgments. After processing, patients can be transferred to primary hospitals, and primary hospitals will undertake the treatment and rehabilitation of non-emergency patients.
Specifically, the hundreds of monitoring beds in the emergency department of Chaoyang Hospital will basically be used to meet the treatment of critical emergency patients, and the non-emergency patients identified after triage in the emergency department will be diverted to relevant cooperative primary hospitals. "This is the way we have just explored. If it goes well, it is expected to change the congestion of the emergency department and prevent the abuse of emergency resources."
According to Guo Shubin’s analysis, this model can take into account the economic and social benefits of both top three hospitals and primary hospitals. For the third-class hospitals, in terms of economic benefits, patients usually spend the most at the beginning of emergency rescue. If the emergency department is occupied by a large number of non-emergency patients at this time, it will obviously reduce the economic benefits of the hospital. In terms of social benefits, the crowded emergency department is also an important cause of public dissatisfaction. For grass-roots hospitals, this model can make them obtain more stable patients, and the economic and social benefits of grass-roots hospitals can naturally be realized.
This model is equivalent to turning the primary hospital into a treatment area in the emergency department of a third-class hospital. Guo Shubin emphasized that the key point is that doctors and nurses must be sent from the emergency department of Chaoyang Hospital to the relevant cooperative hospitals as department directors and head nurses. "This can ensure the position and level of medical decision-making, thus ensuring the equality of medical quality and achieving the purpose of risk sharing and benefit sharing."
Guo Shubin revealed that in the future, Chaoyang Hospital will also enable emergency medical staff of relevant cooperative hospitals to receive regular training from Chaoyang Hospital through telemedicine and other means, and carry out more extensive and comprehensive cooperation in medical teaching and research to effectively improve the business ability of primary hospitals and truly strengthen primary hospitals.
However, will the future emergency department become no longer crowded and "overloaded" because of these practical explorations?
???? "Lookout" Newsweek reporter Zhang Ranran Hu Yongshun